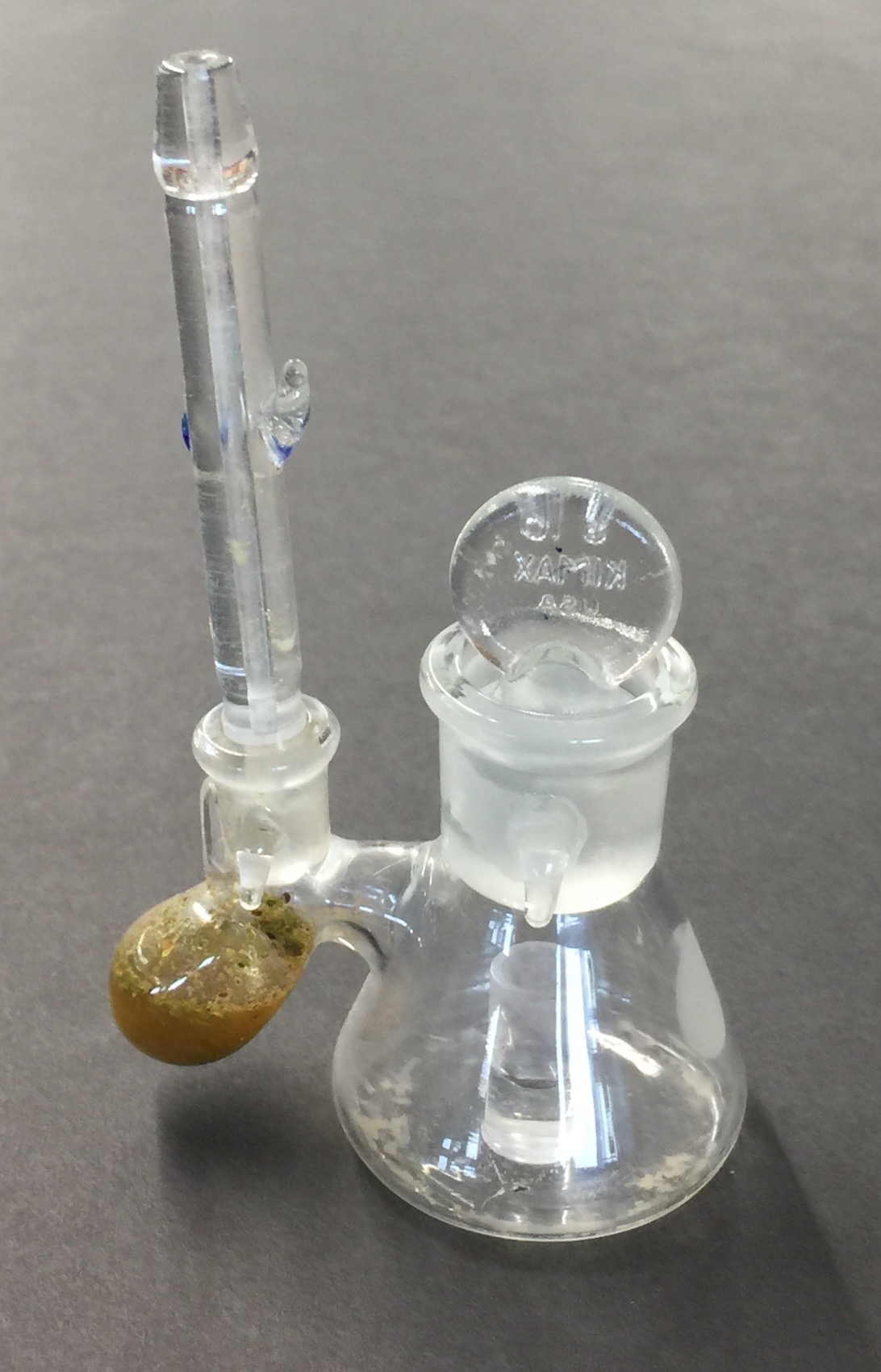
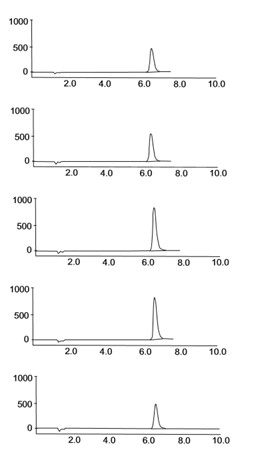
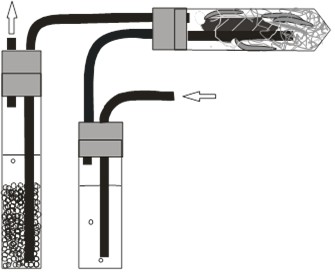
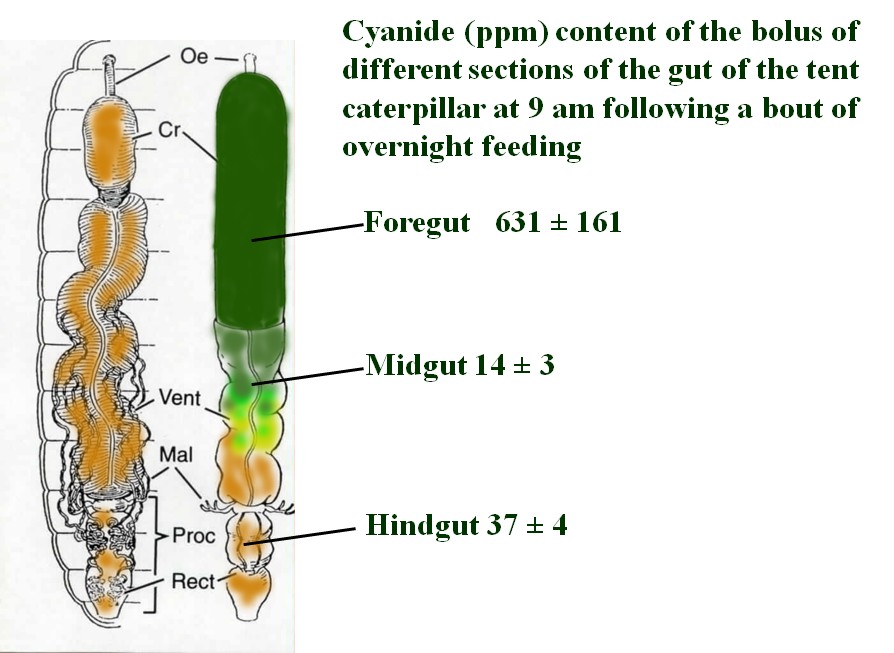
When a cyanogenic sample of leaf, regurgitant, gut contents, or frass is incubated in an acidic buffer, cyanide evolves as the gas HCN. The center well of the Warburg flask is charged with an alkaline solution (NaOH) which traps the gas. The amount of cyanide captured is determined by injecting a sample from the center well into an ion chromatograph.
Fragmented sample in acidic buffer
NaOH in center well traps cyanide emitted from sample
Quantification of the Cyanide Content of a Sample
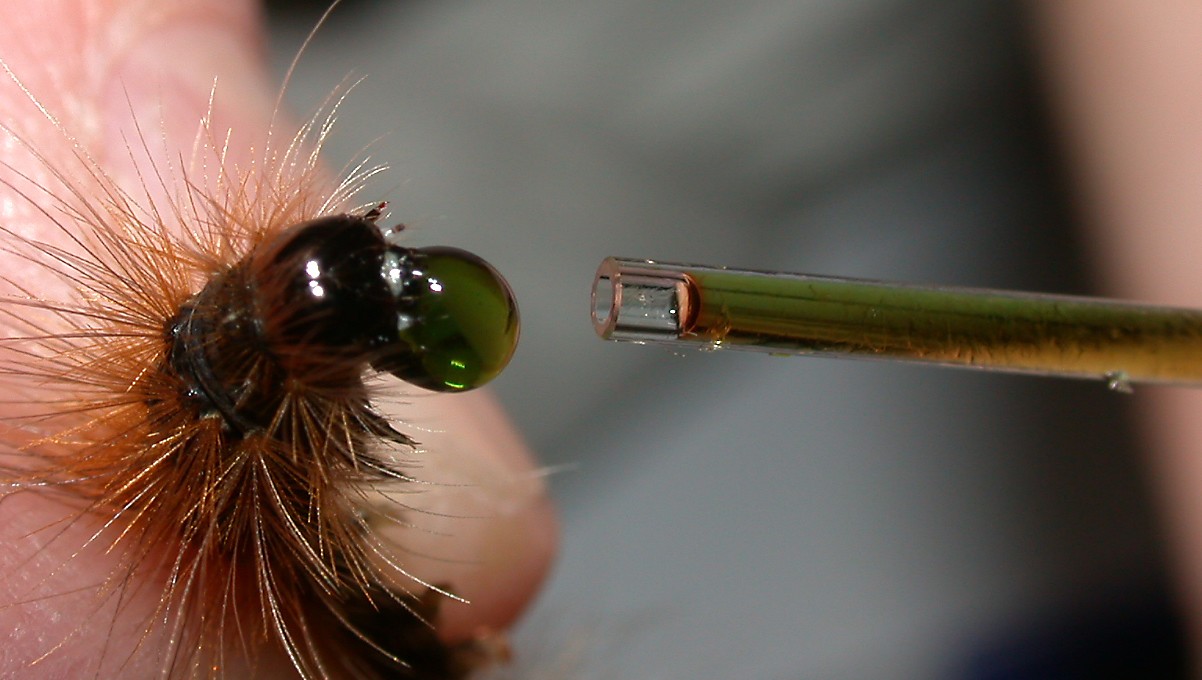
When the caterpillars feed, some of the liberated cyanide gas escapes into the atmosphere. To measure this loss, caterpillars were enlcosed in a vial with leaves and allowed to feed. A stream of air was directed into the feeding compartment and then into a solution of NaOH where the gas was trapped and later sampled. Depending on the species, from 3 - 10% of the cyanide produced when the leaf is macerated by the caterpillars escapes into the atmosphere.