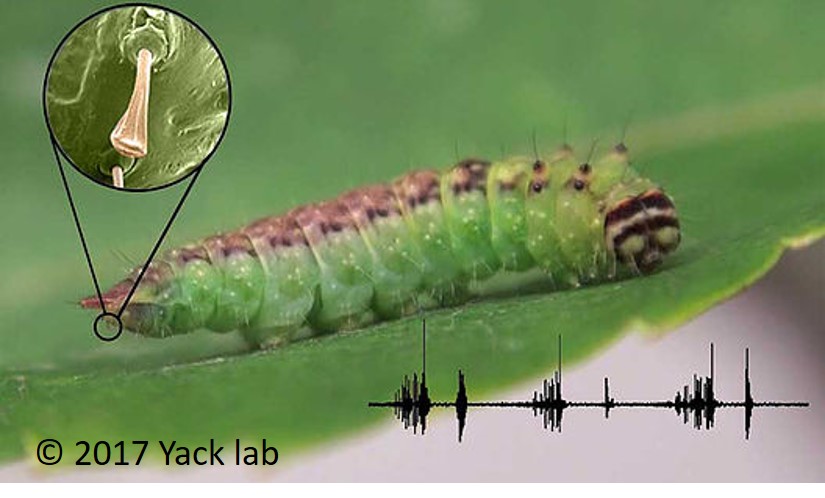
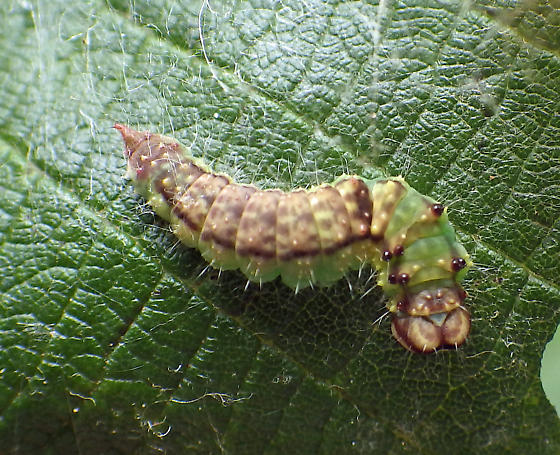
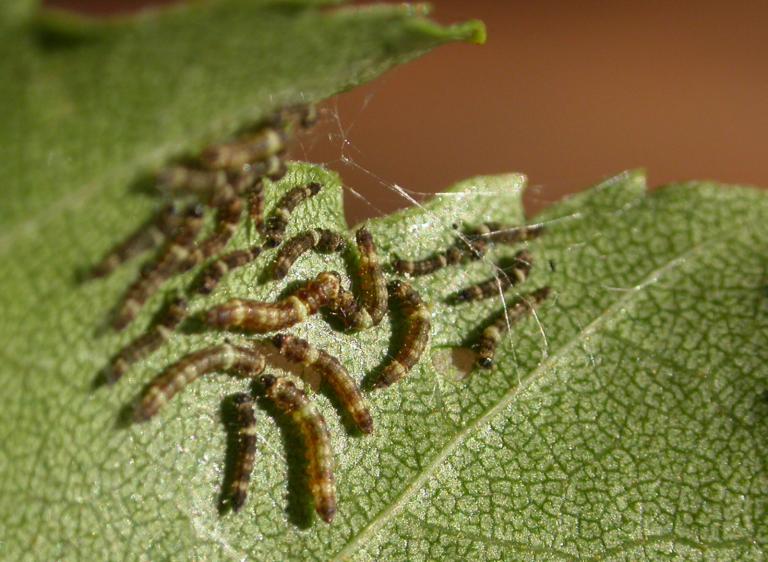
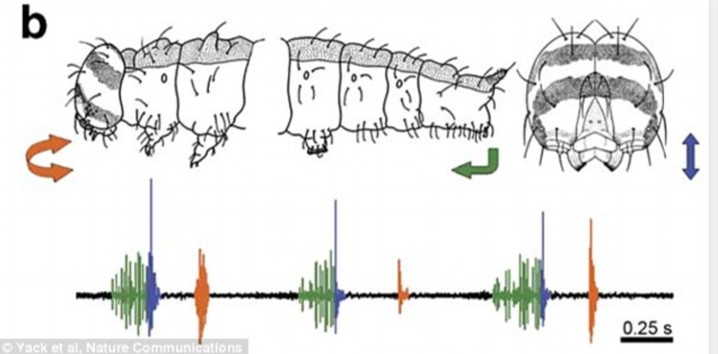
Masked Birch Caterpillar Drepana arcuata (Lepidoptera: Drepanidae)
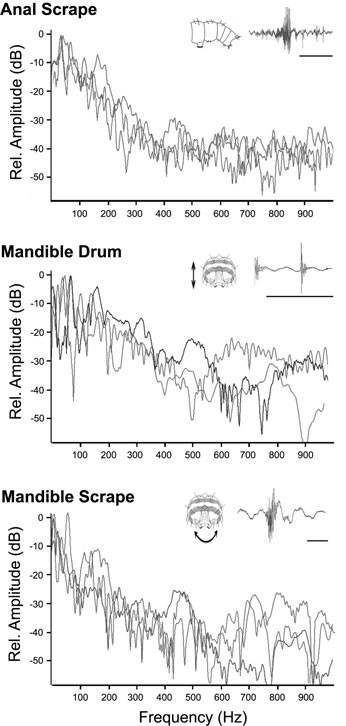
(Right): Frequency spectra for various vibrations produced by D. arcuata on birch leaves.
The older instars of the masked birch caterpillar live solitarily and use vibratory signals to repel rivals.
The caterpillar generates four vibrational signals that affect the behavior of conspecifics: anal scraping, mandible druming, mandible scraping, and buzz scraping, the latter produced when the caterpillar vibrates its body while anal scraping.
As shown in the image and video above, the caterpillar possesses unique structures termed 'anal oars' that are used to generate the scraping vibration.
The younger caterpillars are often found in small groups and studies indicate that the same vibratory signals used by the older caterpillars may facilitate aggregation in younger caterpillars; the signals serving to recruit caterpillars to the feeding sites and shelters of established caterpillars.
A resident caterpillar recruiting a conspecific to its leaf shelter.